The revolution in the advertising industry has been phenomenal with the evolution of the internet. Google being the household name for the internet, has been a boon to marketers from the beginning.
With the introduction of “Google Ads” in the year 2000, it has given a solid platform for advertisers to capture the leads at different stages of sales funnel.
Now the question is, what is Google Ads?
Let’s learn Google Ads!
What is Google Ads?
Google Ads is an advertising platform which connects potential customers who are looking for a product or a service to the advertisers offering the same.
This powerful platform enables advertisers to offer their product or service to the most relevant customers at the crucial stage of their purchase funnel.
Understanding How Google Ads Auction Work
Every time someone searches on Google, an auction happens instantly to decide which ads will show and in what order.
But this auction is not just about who pays the most — it’s about who provides the best overall value to the user.
Let’s imagine this with a fun analogy
Analogy: The Google Ads Talent Show
Imagine Google is hosting a Talent Show.
Many advertisers (performers) want to appear on the stage (Google search results).
But there are limited spots, and Google wants to show only the best acts (ads) for the audience (searchers).
To decide who performs first (top ad), Google judges each advertiser on three key things:
Ad Rank – Your “Final Score” in the Competition
What It Is:
Ad Rank determines where your ad appears on the search results page (or if it appears at all).
Formula (Simplified):
Ad Rank = Bid Amount × Quality Score + Ad Extensions & Context
In Our Analogy:
It’s like your final score in the talent show. Even if you offer (bid) to perform for free (low CPC), if your performance (ad quality) is amazing, you might still get the top spot!
Factors that Affect Ad Rank:
-
Your maximum bid (how much you’re willing to pay per click)
-
Your ad quality (measured by Quality Score)
-
The context of the search (device, location, competition, etc.)
-
Ad extensions (extra info like phone number, links, etc.)
Quality Score – How “Talented” Your Ad Is
What It Is:
Quality Score (QS) is a rating (1–10) of how relevant and useful your ad is to users.
A higher score means Google thinks your ad gives a great experience to people searching.
Components of Quality Score:
-
Expected Click-Through Rate (CTR):
-
How likely users are to click your ad.
-
-
Ad Relevance:
-
How closely your ad matches the keyword searched.
-
-
Landing Page Experience:
-
How relevant, fast, and easy-to-use your landing page is.
-
In Our Analogy:
Think of it like the judges’ opinion of your talent:
-
Are you performing the right song for the audience? (Ad relevance)
-
Do people love your performance and clap? (CTR)
-
Is your backstage area organized and comfortable? (Landing page experience)
Even if your “bid” is lower, a high Quality Score can help you outrank competitors.
CPC (Cost-Per-Click) – What You Actually Pay
What It Is:
CPC is the actual amount you pay each time someone clicks your ad.
It’s not always your maximum bid — Google makes you pay just enough to beat the next advertiser below you.
Formula (Simplified):
Actual CPC = (Ad Rank of the person below you ÷ Your Quality Score) + ₹0.01
In Our Analogy:
It’s like the entry fee you pay to stay on stage.
If your performance (ad quality) is excellent, you pay less to stay in the spotlight because Google rewards you for keeping the audience happy.
Example: Putting It All Together
Let’s say three advertisers are competing for the keyword “best digital marketing course”:
| Advertiser | Max Bid | Quality Score | Ad Rank (Bid × QS) | Position | Actual CPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ₹50 | 10 | 500 | 1st | ₹(420 ÷ 10) + 0.01 = ₹42.01 |
| B | ₹70 | 6 | 420 | 2nd | ₹(300 ÷ 6) + 0.01 = ₹50.01 |
| C | ₹60 | 5 | 300 | 3rd | — |
Advertiser A wins the top spot even with a lower bid, because of a high Quality Score.
This shows how Google rewards relevance and quality — not just high spending.
Simple Summary
| Term | Meaning | Analogy | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ad Rank | Determines your ad position | Final score in the show | Higher score = better visibility |
| Quality Score | Measures ad quality & relevance | Judges’ rating of your talent | Higher score = lower costs |
| CPC | What you actually pay per click | Entry fee to stay on stage | High QS = lower CPC |
Key Takeaway
Google’s auction isn’t a “who-pays-more-wins” system.
It’s a “who-delivers-the-best-user-experience” system.
If your ad is relevant, engaging, and useful, you can:
-
Get higher ad positions
-
Pay less per click
-
And achieve better ROI

Understanding Google Ads Campaign Types
1. Search Campaigns
What It Is:
Search campaigns show text ads on Google’s search results pages when users actively search for keywords related to your business.
Where Ads Appear:
- Google Search results
- Google search partners (like YouTube search or Maps search results)
Ad Format:
- Primarily text ads (can include call, sitelink, and structured snippet extensions)
Best For:
- Driving direct conversions (leads, sales, sign-ups)
- Capturing high-intent users searching for your product or service
Example:
If someone searches “best digital marketing course in Delhi”, your course ad can appear at the top of Google results.
2. Display Campaigns
What It Is:
Display campaigns use visual banner ads to reach users across the Google Display Network (GDN) — a collection of over 2 million websites, apps, and YouTube.
Where Ads Appear:
- Partner websites
- Mobile apps
- YouTube (as banner overlays or side ads)
Ad Format:
- Image banners, responsive display ads, HTML5 animations
Best For:
- Brand awareness and remarketing
- Reaching people earlier in the buying journey
- Staying top-of-mind with past visitors
Example:
A user who visited your course website sees your banner ad later while reading an article on marketing trends.
3. Video Campaigns
What It Is:
Video campaigns run primarily on YouTube and across Google video partners. These use video ads to tell stories, demonstrate products, or educate audiences.
Where Ads Appear:
- Before, during, or after YouTube videos (TrueView, skippable or non-skippable)
- YouTube search results
- Partner sites and apps
Ad Format:
- Skippable and non-skippable video ads
- Bumper ads (6-second videos)
- In-feed video ads (appear in YouTube search results)
Best For:
- Brand awareness
- Product storytelling
- Engaging visual campaigns and remarketing
Example:
Your video explaining “How to start a digital marketing career” plays before a related YouTube video.
4. Shopping Campaigns
What It Is:
Shopping campaigns promote your products with an image, price, and brand name directly on Google Search and Shopping tab.
Where Ads Appear:
- Google Search results (above or beside text ads)
- Google Shopping tab
- YouTube and Display Network (for Smart Shopping)
Ad Format:
- Product-based ads with visuals and price details pulled from your product feed in Merchant Center
Best For:
- E-commerce businesses
- Driving product sales with visual, price-focused ads
Example:
When someone searches “buy running shoes online”, your product ad with image, price, and brand shows up at the top.
5. App Campaigns
What It Is:
App campaigns promote mobile app installations or in-app actions across Google properties.
Where Ads Appear:
- Google Search
- Google Play Store
- YouTube
- Google Display Network
- Discover feed
Ad Format:
- Automatically generated using your app’s assets (text, images, videos)
Best For:
- Increasing app downloads
- Encouraging app engagement or in-app purchases
Example:
Your app ad shows up in Google Play suggestions when users look for marketing learning apps.
6. Performance Max Campaigns
What It Is:
A newer campaign type that combines automation and machine learning to run ads across all Google networks — Search, Display, YouTube, Discover, Gmail, and Maps — from one campaign.
Where Ads Appear:
Everywhere Google serves ads.
Ad Format:
Automatically mixes and matches your assets (text, images, videos).
Best For:
- Businesses that want a single, AI-driven campaign to maximize performance across channels.
- Conversions, lead generation, or e-commerce sales.
Example:
Google’s AI decides whether to show your ad as a search ad, display banner, or YouTube video depending on user intent and likelihood to convert.
What are the various ad formats available?
With Google, your ads can become as interesting as possible. Ads provides you with a plethora of ad formats to choose from;
- Text Ads: Simple yet effective text ads with 2 headlines of 30 characters each and a description of 80 characters. Make these text ads more compelling by using ad extensions such as site extension, call extension, location extension, message extension etc.

- Image Ads: Draw the attention of users on more than 2 million websites by using attractive image ad formats such as static graphics, ads in .gif, flash ads etc. This format is available only for display network.
- Responsive Ads: The major challenge for advertising in display network is to fit your ad to the available ad space on third-party websites. To make your life easy, Google Ads provides “Responsive Ads” which automatically adjusts the size & format according to the ad space available and it also considers the device & the internet speed of the user to determine the ad format which loads faster.
- Shopping Ads: This ad format is suitable for advertisers having a large inventory. This ad format showcases the image of the product, title, price, store name etc.
- Call only Ads: If most of your business transactions initiated via phone call, then this ad format is what you need. Business phone number is shown in the headline of the ad. When a user clicks on the ad, the call is connected to your business directly instead of loading your website. Note that this format is available only on the devices which can make a phone call.
Above mentioned are the widely used ad formats. With the evolution of Ads Platform, Google is introducing new ad format very frequently. Choose the right format for your business and make compelling ads.
The Importance of Keywords in Google Ads
Keywords are the foundation of every Google Ads campaign. They connect what people are searching for with the ads you show. Choosing the right keywords ensures your ads appear in front of the right audience at the right time, maximizing your return on investment (ROI).
Why Keywords Matter
-
They Define Who Sees Your Ads:
Every time a user types a search query, Google matches it to relevant keywords in advertisers’ accounts. The closer the match, the higher the chance your ad will appear. -
They Affect Ad Relevance & Quality Score:
Highly relevant keywords improve your Quality Score, which leads to better ad positions and lower costs per click (CPC). -
They Control Cost & Performance:
Right keywords attract people likely to convert; wrong ones waste your budget. Keyword selection determines whether your campaign succeeds or fails. -
They Guide Campaign Structure:
Well-organized keyword groups (ad groups) make your ads more targeted and improve user experience — leading to better CTRs and conversion rates.
How to Conduct Keyword Research
Keyword research helps you discover the terms your target audience actually uses to find your products or services.
Here’s a step-by-step approach:
Step 1: Understand Your Business and Audience
Before using tools, list out what your business offers and what your customers might search for.
Ask yourself:
-
What problems do my customers want to solve?
-
What words or phrases would they use to describe my service?
Example:
For a digital marketing course, people might search for:
“digital marketing course,” “online marketing training,” “SEO course in Delhi,” etc.
Step 2: Use Keyword Research Tools
Use Google’s tools and other platforms to find real search data.
Popular Tools:
-
Google Keyword Planner (free inside Google Ads)
-
Ubersuggest
-
Ahrefs or SEMrush
-
Google Trends
What to Look For:
-
Search Volume: How many people search for that keyword each month
-
Competition Level: How many advertisers are bidding for it
-
CPC (Cost-Per-Click): How expensive each click may be
-
User Intent: What users want when they search (to learn, compare, or buy)
Step 3: Identify Keyword Intent
Not all keywords are equal — each type serves a different purpose.
| Type | Example | Intent |
|---|---|---|
| Informational | “What is digital marketing?” | Research/learning |
| Navigational | “Digital Vidya course” | Looking for a specific brand |
| Commercial | “Best digital marketing course in India” | Comparing options |
| Transactional | “Buy digital marketing course online” | Ready to purchase |
Tip: Focus more on commercial and transactional keywords for conversions, and use informational keywords for content marketing or remarketing strategies.
Step 4: Choose the Right Match Types
Google Ads allows different keyword match types to control how closely a search must match your keyword.
| Match Type | Example Keyword | What It Does |
|---|---|---|
| Broad Match | digital marketing course | Shows ads for related searches like “online marketing classes” |
| Phrase Match | “digital marketing course” | Shows ads for searches that include the phrase, like “best digital marketing course in Delhi” |
| Exact Match | [digital marketing course] | Shows ads only for that exact term or close variants |
Tip: Start with Phrase or Exact Match to maintain control and avoid irrelevant clicks.
Step 5: Use Negative Keywords
Negative keywords prevent your ads from showing for irrelevant searches.
For example, if you sell paid courses, add negative keywords like:
-
“free”
-
“PDF”
-
“jobs”
This helps you save budget and improve targeting accuracy.
Step 6: Continuously Optimize
Keyword research isn’t a one-time task.
-
Monitor search terms report in Google Ads.
-
Remove low-performing or irrelevant keywords.
-
Add new high-converting terms regularly.
Key Takeaway
The success of your Google Ads campaign depends largely on how well you choose your keywords.
By selecting high-intent, relevant, and cost-effective keywords — and managing them strategically — you ensure your ads reach the right audience, drive quality traffic, and deliver maximum ROI.
How to Structure an Google Ads Account?
Now that you have a decent understanding of what is Google Ads, its time to learn how to use Google Ads.
It is very crucial learn to structure your Ads account duly to get the maximum benefit of Ads. In order to organize the account, Ads has 3 levels:
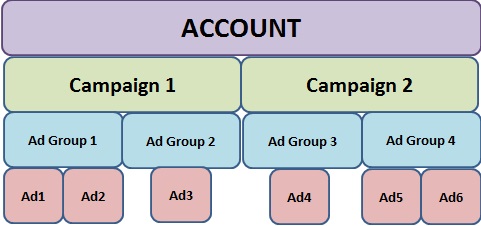
The pulse of an Google Ads Account is its keywords.
Keywords form the base of your account. Google Ads has a very handy tool to discover the most important keywords for your business called as “Keyword Planner”.
This tool gives you the plethora of keywords based on the information you have provided such as sample phrase/keyword, product/ service, website or category of business. Once the set of keywords are ready, it’s time to organize the account.
Campaign
Every campaign should have a unique objective. A campaign has to be created for every product or service your business offers. A campaign consists of a collection of ad groups. Following settings are available at Campaign level;
- Type of campaign such as Search Only Campaign, Display Campaign, Search with Display select, Call Only Campaign etc.
- Budget allocation
- Geographical location where you want ads to show
- Type of bidding strategy
- Other top-level settings which affect all the ad groups under the campaign
Attend Live Orientation Session
Ad Group
Ad Group consists of a set of keywords and ads. There is more than one way to structure your ad groups. Some of the widely followed methods are;
- Structure ad groups based on the set of keywords having similar theme
- Structure ad groups based on the subcategory of product or service
- Structure ad groups based on the different location where you want to show ads
Well organized ad groups help you to serve most relevant ads for the search query.
Keywords
Keywords are the foundation of an Google Ads account. Keywords are grouped into Ad groups based on their theme. It is impossible to list all the exact keywords your customers search in the account. Hence, Google Ads has given various keyword matches to ensure to reach as broad or as specific audience as you want.
A bid is the amount you are willing to pay to Google for every click or 1000 impression (based on the bidding strategy selected at campaign level) of your ad. Bidding is done at the keyword level. To help you start with bidding, keyword planner tool provides you with a suggested bid for every keyword.
Ads
Every ad group can have more than 1 variation of an ad. Based on the type of campaign, various ad formats are made available.
It is advisable to have at least 3 ads per ad group and keep optimizing the performance of ad groups by experimenting with new ads copies.
Google has a very stringent ad policy which an advertiser needs to abide. Every ad is reviewed by AdWords before publishing.
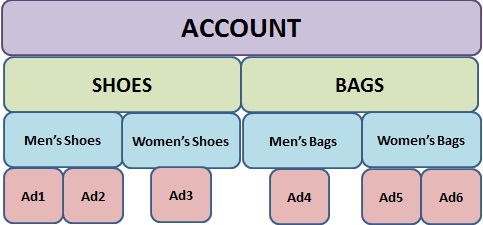
Let’s look into an illustration of structuring an AdWords account:
Imagine you have a boutique where you sell shoes and bags for men and women.
How Google Ads Works?
In order to have a distinct understanding of what is Google Ads, it is very crucial to know how Google Ads works.
When you search on Google, most often you will be shown 4 ads on top of the page. These 4 ads have defeated other competitors in the ad auction to secure their position.
Let’s explore how Ads work:
What happens in Google Ads Auction?
Every time a search happens in Google, Ads takes into account all the advertisers who are bidding on the keyword and calculates Ad Rank for the keyword.
Ad Rank = Quality Score of the Keyword x Bid
Quality Score is the aggregate score given to a keyword based on 3 factors; Ad relevancy to the search query, landing page experience and expected click-through rate (CTR).
Those ads which are above the ad rank threshold are selected to be shown in the search result. The Position of ads are decided based on the ad rank – the first position to the highest ad rank & last position to the lowest ad rank.
Fair Enough!
How much do you pay to Google Ads?
Through bids, you indicate Google Ads, the maximum amount you want to pay, but that is not actually you pay. Most of the times it is less than your bid.
The amount you pay to AdWords for every click is just enough to hold your position from your next competitor.
Let’s understand this practically;
| Position | QS | Bid ($) | Ad Rank | Actual CPC |
| 1 | 7 | 20 | 140 | 19.1 |
| 2 | 9 | 15 | 135 | 13.1 |
| 3 | 6 | 30 | 120 | 27.1 |
| 4 | 4 | 18 | 108 | 18 |
Actual CPC = (Ad Rank of the advertiser below you / Your Quality Score) + $0.01
In the above illustration, every advertiser is paying less than the actual bid (Except the advertiser in the last position).
Lower the ad rank of your competitor and higher your quality score, lower you pay to AdWords.
Benefits of Advertising Online with Google Ads
Advertisers have been exploiting Google Ads since 2000 and benefiting their business enormously. There are numerous benefits of advertising on AdWords.
I have narrowed down the top 4 benefits on my list;
Measure Everything
You have placed a billboard in the 2 most happening locations of your city.
Now there is a leap in your sales, great! But, you are not sure which location’s billboard is driving your sales, is it location1 or location2 or both or none? With conventional marketing, these questions are always unanswered!
In Google Ads, every action is measurable. Right from impressions, clicks, time spent on your website, conversion etc.
It is very important to channelize your marketing budget in the right direction. With Google Ads, you can easily measure and take a data-driven decision to optimize your performance and increase your ROI
Capture Right Audience at the Right Time
Let’s take the billboard example again. You are into the business of denim, you want to capture the attention of the young crowd. You decide to place the billboard in a location where most of the colleges of your city are located. That’s it, you can’t-do anymore targeting.
In Google Ads, you can capture the denim seekers (Right Audience), when they are searching for denim to purchase (Right Time).
This gives an immense targeting option to advertisers to offer their product to the right audience at the right time.
Remarketing
A user surfed for t-shirt section on your website and left the website without buying the product. With AdWords’ Remarketing campaign, you can retarget this user with a customized ad showing the new arrivals of t-shirt or offer a special discount.
In this way, you can re-engage the user and increase your chance of conversion.
Reach Potential Customers on Display Network
Advertisers can reach a more qualified audience on Display network with advanced targeting features such as custom affinity audience and in market audience.
Web users are categorized based on their internet behavior into different categories. Advertisers can select a relevant category or customize their own category to target the audience.
For example, let’s say I am reading about upcoming cricket matches, cricket scores, watching cricket on internet, there is a high chance that I can see an ad which is selling customized cricket t-shirts.
You might discover a new benefit every day. The key for success in Google Ads is effective utilization of the platform, measurement of the performance and data-driven decisions.
With having complete knowledge of what is Google AdWords, you should also be aware of what is Google Ads Express.
At the end, hope this Google Ads tutorial has given you the answer for What is Google AdWords? and How Google Adwords Works?
Photo Credits: Wordstream, adnabu, thrivesearch


